Choosing The Correct Voltage And Frequency For Industrial Fans
2025-07-08
Selecting the appropriate voltage and frequency for industrial fans is a crucial step in ensuring reliable operation and efficient performance. Whether dealing with a high pressure centrifugal blower, a high pressure fan, or an exhaust blower, matching the electrical requirements to the fan’s design and operating environment helps prevent mechanical issues, energy waste, and premature wear.

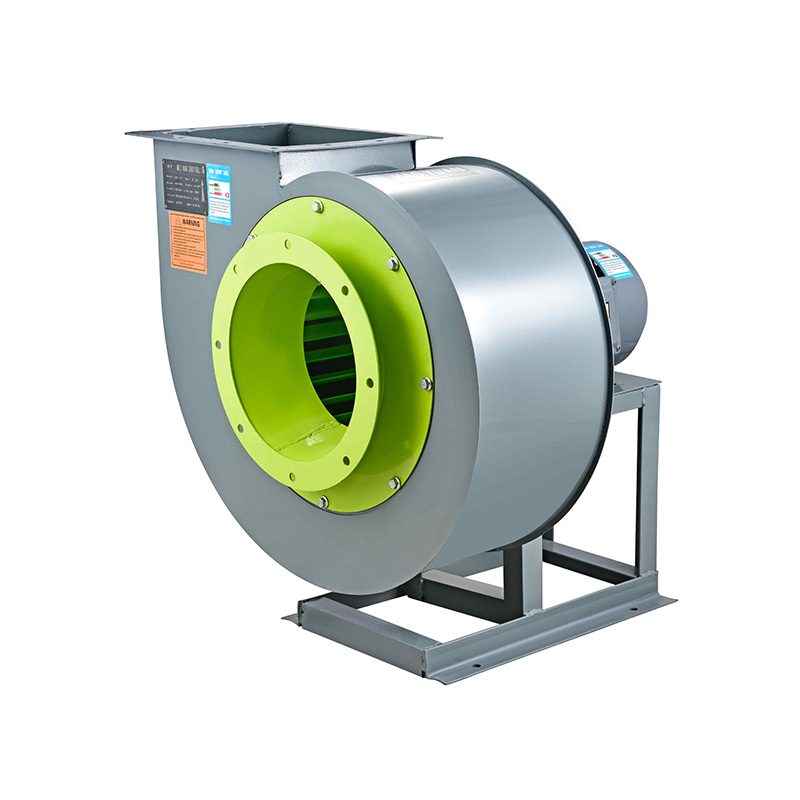
Industrial fans are commonly used across many sectors, including manufacturing, HVAC, mining, and chemical processing. Each of these fans, especially those with specialized features like a high pressure centrifugal blower, relies heavily on stable electrical input. Voltage and frequency specifications directly influence motor speed, torque, and overall functionality. Therefore, understanding how to choose the correct voltage and frequency can enhance system longevity and reduce operational disruptions.
Voltage refers to the electrical potential supplied to the fan motor, while frequency indicates the number of alternating current (AC) cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz). Industrial fans are usually designed for specific voltage and frequency ratings, often standardized by country or region. For example, in North America, many industrial fans operate at 60 Hz with voltages around 230V or 460V, whereas in Europe and parts of Asia, 50 Hz and 400V are more common. Using a high pressure fan designed for 50 Hz on a 60 Hz supply can result in performance deviations that affect airflow and pressure output.
One of the common issues when the wrong voltage or frequency is applied is overheating. Motors in a high pressure centrifugal blower depend on correct input to maintain proper speed and torque. If the voltage is too low, the motor may draw excessive current to compensate, causing increased heat buildup and reducing motor life. Conversely, too high a voltage can cause insulation breakdown or mechanical stress. Likewise, a frequency mismatch can cause the motor to run faster or slower than intended, affecting the fan’s ability to generate required pressure and volume. This is especially critical in exhaust blowers used to remove contaminants or maintain airflow in enclosed spaces.
When selecting a fan for an application, always verify the voltage and frequency ratings specified by the manufacturer. Industrial fans like high pressure fans often come with nameplates indicating voltage and frequency ranges that the motor can safely handle. It is essential to consult these ratings to avoid mismatches. For example, a high pressure centrifugal blower rated for 400V, 50 Hz should not be connected directly to a 460V, 60 Hz supply without proper adjustments or equipment such as frequency converters.
Frequency converters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), are often employed to adapt the power supply to the motor’s requirements. These devices allow the adjustment of frequency and voltage supplied to the fan motor, enabling flexible speed control. This capability is valuable for exhaust blowers that need variable airflow based on operational demands. By controlling frequency and voltage, VFDs help maintain consistent performance, reduce energy consumption, and less mechanical stress on the fan components.
Another important factor to consider is the compatibility of the electrical infrastructure with the fan’s voltage and frequency. The power supply system must reliably deliver the required electrical parameters under different load conditions. In some industrial environments, voltage fluctuations or frequency variations can occur due to heavy equipment operation or grid instability. Installing protective devices such as voltage stabilizers or surge protectors can safeguard fans like high pressure centrifugal blowers from electrical damage.
It’s also worth noting that selecting the correct voltage and frequency supports regulatory compliance and safety standards. Electrical codes and industrial guidelines often specify requirements for motor installations to prevent hazards. Ensuring that the high pressure fan or exhaust blower operates within designated voltage and frequency parameters contributes to a safer working environment and reduces risks of downtime caused by electrical faults.
Furthermore, attention to voltage and frequency helps optimize the overall energy efficiency of industrial ventilation systems. When a fan runs at the intended speed, it uses power more effectively, less waste. For example, a high pressure centrifugal blower that is undersupplied in voltage may not achieve its designed airflow, forcing the system to run longer or at higher speeds to compensate, which can increase energy consumption and operational costs.
In summary, choosing the correct voltage and frequency for industrial fans is fundamental to achieving reliable and efficient ventilation performance. High pressure centrifugal blowers, high pressure fans, and exhaust blowers all depend on electrical input matching their design specifications to function properly. Paying close attention to voltage and frequency ratings, consulting manufacturer guidelines, and considering the use of devices like frequency converters can help maintain system stability and prolong fan life. Additionally, ensuring the power supply is stable and compliant with local electrical standards further supports smooth operation. Taking these factors into account ultimately leads to better maintenance outcomes, energy savings, and a safer industrial environment.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى