Common Causes Of Fan Bearing Failure And Solutions
2025-07-08
Fan bearings are critical components that enable smooth and efficient operation of various types of fans, including low noise ventilation fans, boiler fans, and centrifugal blower fans. Bearing failure is one of the pilot causes of downtime and reduced equipment life in these systems. Understanding the common causes of fan bearing failure can help operators and maintenance teams implement effective solutions to extend the service life of their fans and maintain system reliability.

One common cause of bearing failure in low noise ventilation fans is contamination. Dust, dirt, or moisture can enter the bearing housing and degrade the lubricant, causing increased friction and wear. Since low noise ventilation fans often operate in environments where quiet airflow is essential, even small amounts of contamination can disrupt bearing performance, pilot to increased noise and eventual failure. Regular inspection and cleaning of the fan and surrounding area can help less contamination risks. Additionally, using sealed or shielded bearings can prevent contaminants from entering the bearing assembly.
Another factor affecting the longevity of boiler fans is improper lubrication. Boiler fans typically operate under demanding thermal conditions, which can cause lubricant breakdown if not managed properly. Without adequate lubrication, metal-to-metal contact occurs within the bearing, pilot to rapid wear and overheating. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's lubrication schedules and use lubricants suited for high-temperature applications common in boiler fans. Automated lubrication systems can be beneficial for maintaining a consistent lubricant supply and reducing the chances of human error.
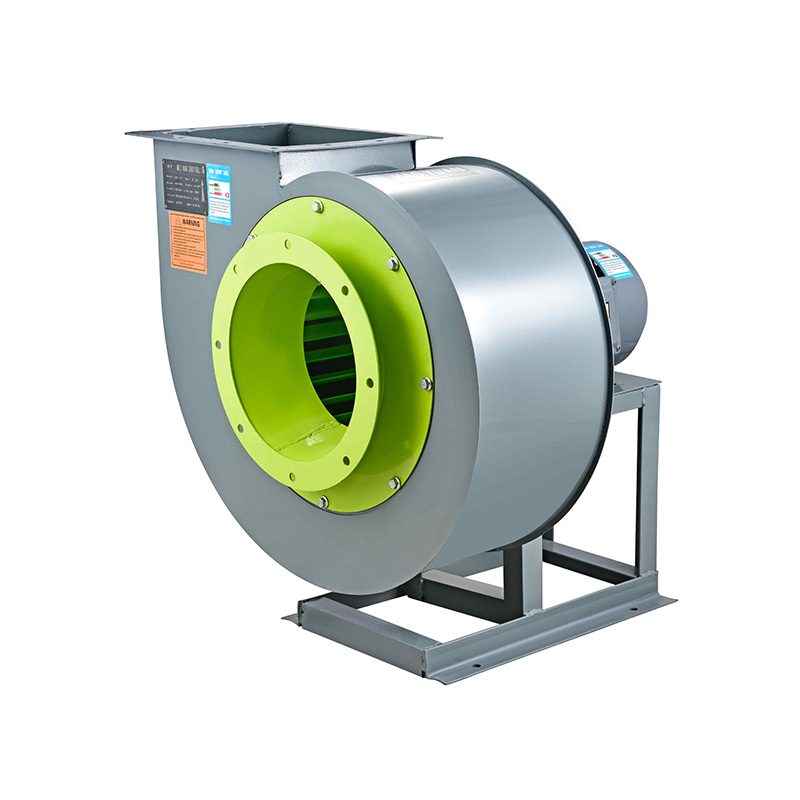
Misalignment is a frequently overlooked cause of bearing failure in centrifugal blower fans. If the fan shaft is not properly aligned with the motor or driven equipment, excessive radial and axial loads can be imposed on the bearing. These loads accelerate wear and can cause premature bearing damage. Precision alignment during installation, combined with periodic checks, helps ensure that the centrifugal blower fan operates smoothly. Laser alignment tools have become popular in maintenance to achieve and maintain correct alignment efficiently.
Vibration is another major contributor to bearing issues across low noise ventilation fans, boiler fans, and centrifugal blower fans. Excessive vibration can arise from unbalanced fan blades, worn components, or external sources like building movement. Vibration increases stress on the bearings and can cause fatigue failure over time. Regular vibration analysis can detect abnormalities early, allowing maintenance teams to take corrective actions such as balancing the fan or replacing worn parts before bearing damage occurs.
Temperature bads also play a role in bearing failure, particularly in boiler fans, which often work in high-heat environments. Bearings exposed to temperatures beyond their design limits can experience lubricant breakdown and material degradation. Similarly, low noise ventilation fans used in cold environments may suffer from lubricant thickening, reducing bearing mobility. Selecting bearings with suitable temperature ratings and using appropriate lubricants can mitigate these risks. In some cases, additional cooling or heating measures may be necessary to maintain good operating temperatures.
To address these common causes, it is important to establish a regular maintenance routine for all types of fans, including low noise ventilation fans, boiler fans, and centrifugal blower fans. This routine should include bearing inspections for signs of wear, lubricant condition checks, alignment verification, and vibration monitoring. Predictive maintenance tools, such as ultrasonic detectors and thermal cameras, can provide valuable early warnings about bearing health and prevent unexpected failures.
In addition to maintenance, investing in quality bearings designed for specific fan applications can make a significant difference. For example, boiler fans benefit from high-temperature resistant bearings, while low noise ventilation fans require precision bearings designed to produce less operational noise. Centrifugal blower fans often demand bearings capable of handling radial loads and moderate axial loads due to their operating conditions.
Replacing worn or damaged bearings promptly is also critical. Delaying bearing replacement can lead to more severe damage, not only to the bearing itself but also to the fan shaft, housing, and connected components. This can increase repair costs and downtime. When installing new bearings, it is essential to follow proper installation procedures, including correct handling, lubrication, and alignment.
In conclusion, bearing failure in fans such as low noise ventilation fans, boiler fans, and centrifugal blower fans is often caused by contamination, improper lubrication, misalignment, vibration, and temperature bads. Addressing these issues through preventive maintenance, proper bearing selection, and timely repairs can significantly improve fan reliability and service life. By understanding and acting on these common causes, facility managers and maintenance teams can ensure their ventilation and blower systems operate efficiently and with small disruption.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى