Comparison Between Forward And Backward Curved Fans
2025-07-08
Understanding their differences helps engineers and maintenance teams make better decisions, especially when choosing fans for systems like high speed ventilation fan setups or industrial exhaust blower fan units.

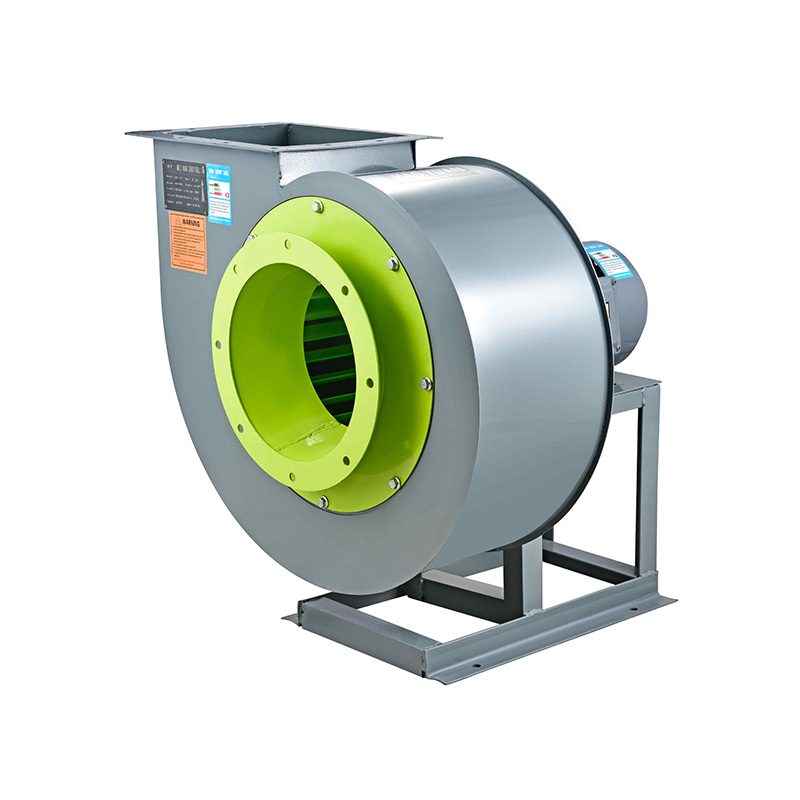
Forward curved fans, as the name suggests, have blades that curve in the direction of the fan's rotation. These fans are generally known for moving large volumes of air at relatively low static pressures. They operate quietly and are commonly used in HVAC systems where space is limited and noise is a concern. In contrast, backward curved fans have blades that sweep away from the direction of rotation. These fans are designed to handle higher static pressures and typically offer greater energy efficiency under those conditions.
When selecting a centrifugal air fan for a high speed ventilation fan system, one must consider how each design behaves under different loads. Forward curved fans can become less efficient as system resistance increases, which may lead to motor overloading if not sized correctly. On the other hand, backward curved fans have a non-overloading power characteristic, meaning that the power draw decreases if resistance rises beyond a certain point. This makes them a safer choice in systems where pressure conditions may fluctuate unexpectedly.
In an industrial exhaust blower fan setup, reliability and consistent performance under high-pressure conditions are often required. Backward curved fans are typically favored in such applications due to their sturdier construction and ability to maintain performance across a broader range of system pressures. These fans are well-suited for environments where dust, fumes, or hot gases need to be continuously extracted, such as factories, commercial kitchens, or paint booths.
However, forward curved fans still hold value in certain environments. In small-scale ventilation units or where lower static pressure is sufficient, a high speed ventilation fan equipped with forward curved blades can offer compactness and quiet operation. The choice ultimately depends on the specific performance goals and spatial limitations of the project.
Maintenance is another important aspect to consider. A centrifugal air fan with backward curved blades typically requires less frequent maintenance because of its self-cleaning nature. The design naturally discourages the buildup of debris on the blades, which is a benefit in dirty air applications. Forward curved fans, with their densely packed blades, can be more susceptible to clogging in dusty environments. This is especially relevant in industrial exhaust blower fan systems, where airborne contaminants are present.
When energy consumption is a concern, backward curved fans often provide better energy performance over time. Their higher efficiency at medium to high static pressures makes them ideal for continuous operation scenarios. Whether it’s a centrifugal air fan used in an air handling unit or a high speed ventilation fan in a factory, selecting a fan with a lower power draw can significantly reduce operating costs in the long term.
Despite these distinctions, both types of fans have their place in industrial settings. A backward curved centrifugal air fan is commonly installed in large-scale industrial exhaust blower fan systems where durability and pressure handling are priorities. Meanwhile, forward curved fans still serve well in applications such as small air conditioners, low-pressure ventilation ducts, or smaller high speed ventilation fan units where footprint and noise reduction are key factors.
In summary, while forward and backward curved fans are both members of the centrifugal air fan family, their differences are notable. Forward curved fans favor volume and compactness, making them suitable for low-pressure, low-noise applications. Backward curved fans, with their resilience and adaptability, are often the go-to solution for high-demand environments like industrial exhaust blower fan installations. Understanding these characteristics allows engineers to better match the right fan to the right job—ensuring that whether it’s a high speed ventilation fan or a large centrifugal system, the airflow stays reliable and efficient.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى