Energy-Efficient Fan Options For Industrial Facilities
2025-07-08
In industrial facilities, ventilation and air circulation are critical for maintaining a safe and productive environment. Selecting energy-efficient fan options can significantly reduce operational costs while ensuring adequate airflow. Among the many types available, the high speed industrial fan, rotor fan, centrifugal fan, and axial fan are commonly used due to their reliability and adaptability to various industrial applications.
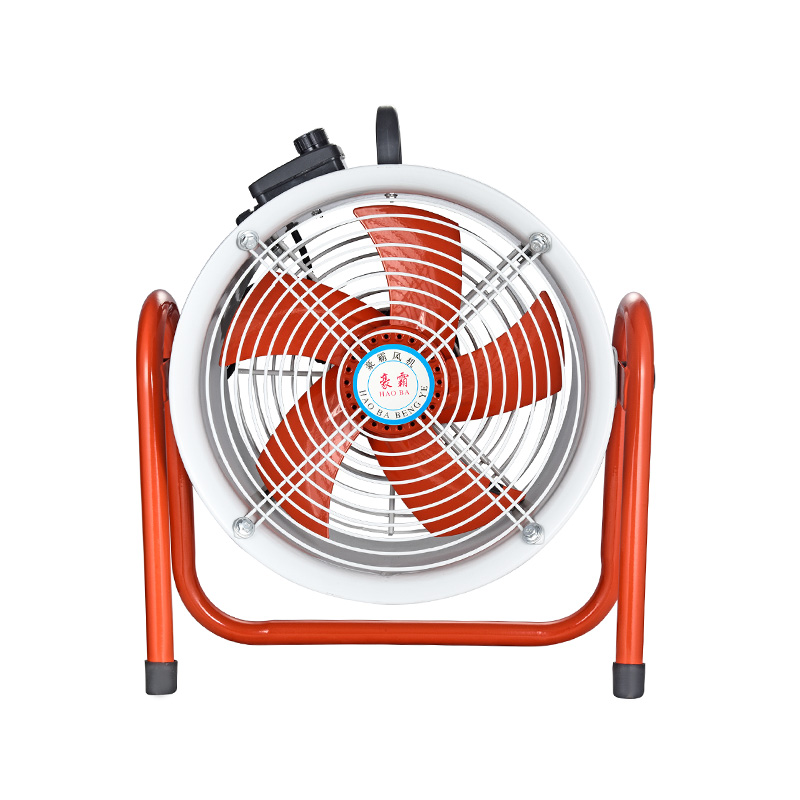

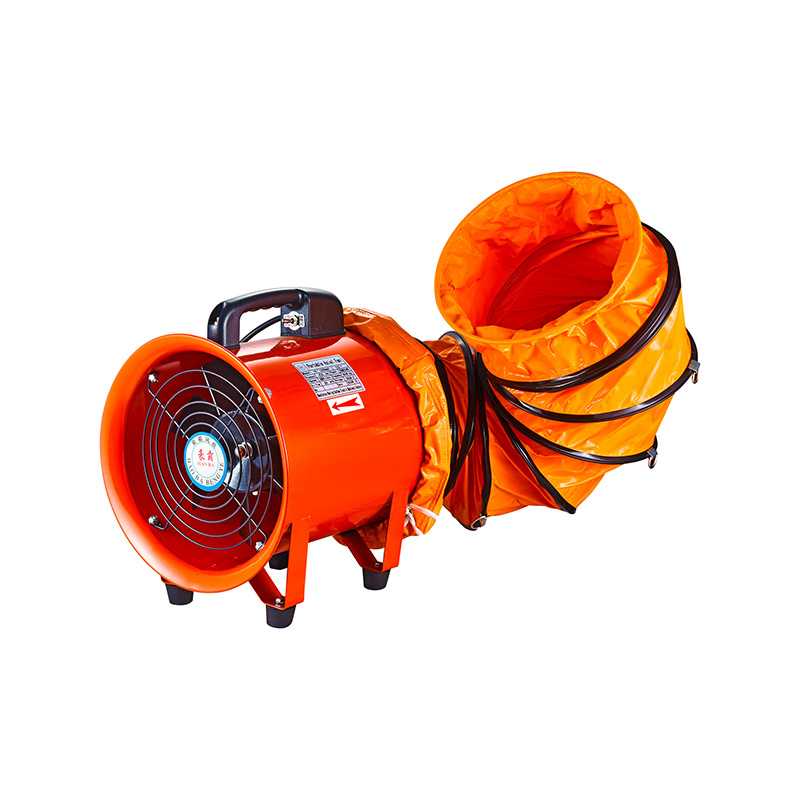
A high speed industrial fan is designed to move large volumes of air rapidly, making it suitable for areas where quick air exchange is necessary. These fans often operate at speeds that generate strong airflow, which helps in cooling equipment, ventilating workspaces, and reducing airborne contaminants. Because they operate at high speeds, selecting energy-efficient models that maintain airflow while consuming less power is essential. Newer designs focus on aerodynamic improvements that allow these fans to move air more efficiently without requiring excessive motor power.
The rotor fan is a variation that integrates the motor and impeller into a single rotating assembly. This design reduces mechanical losses and simplifies maintenance. In many industrial facilities, rotor fans are valued for their compact size and quieter operation compared to some traditional fan types. The efficiency of a rotor fan depends heavily on the quality of its components and the precision of its engineering. Choosing rotor fans with well-designed blades and high-quality motors can enhance energy savings over time.
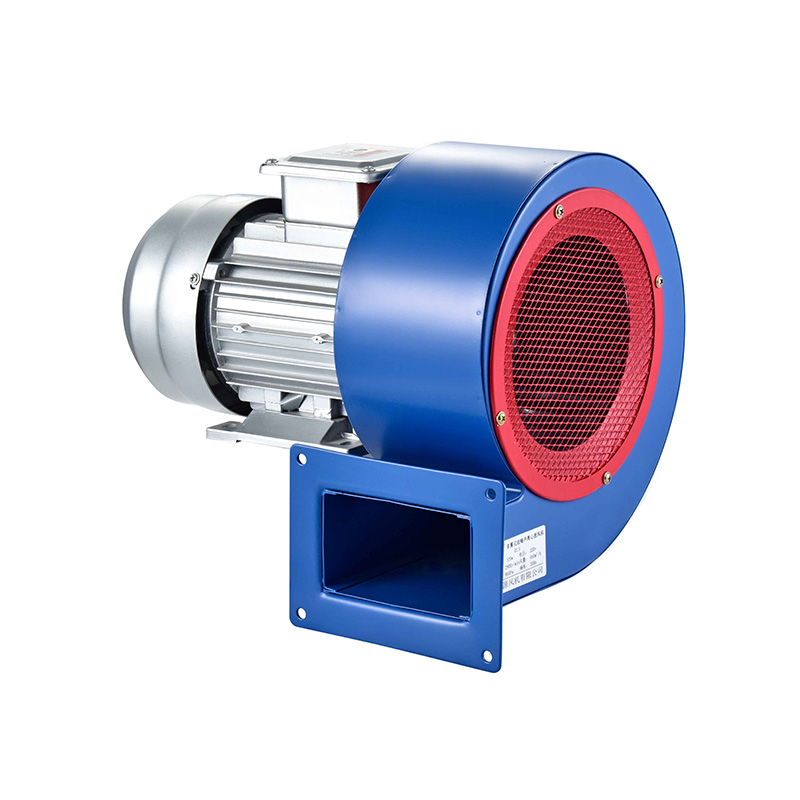
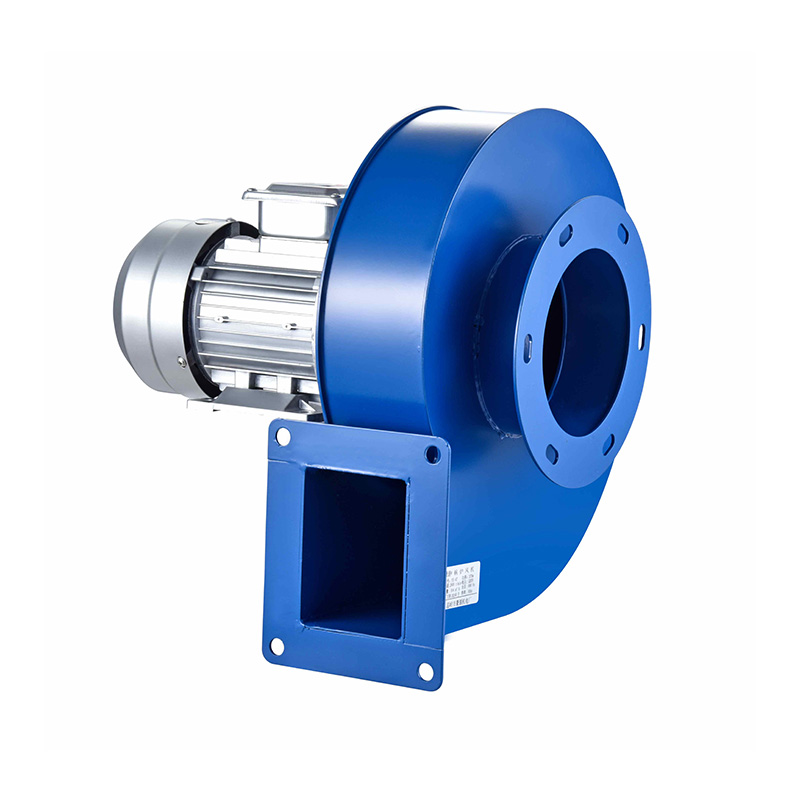
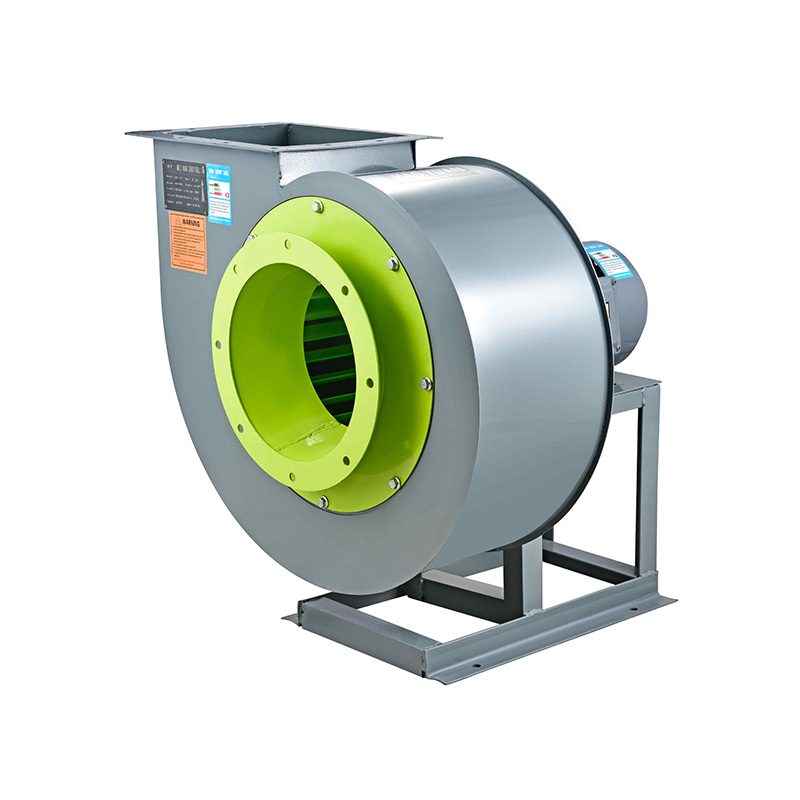
When comparing fan types, the centrifugal fan and axial fan serve distinct roles based on airflow requirements and space constraints. A centrifugal fan uses a rotating impeller to draw air into the center and push it out at a 90-degree angle through a volute or scroll housing. This design generates higher pressures, making centrifugal fans suitable for applications requiring air to move through filters, ducts, or other resistance points. Their ability to maintain airflow against resistance makes them a popular choice in many industrial ventilation systems.
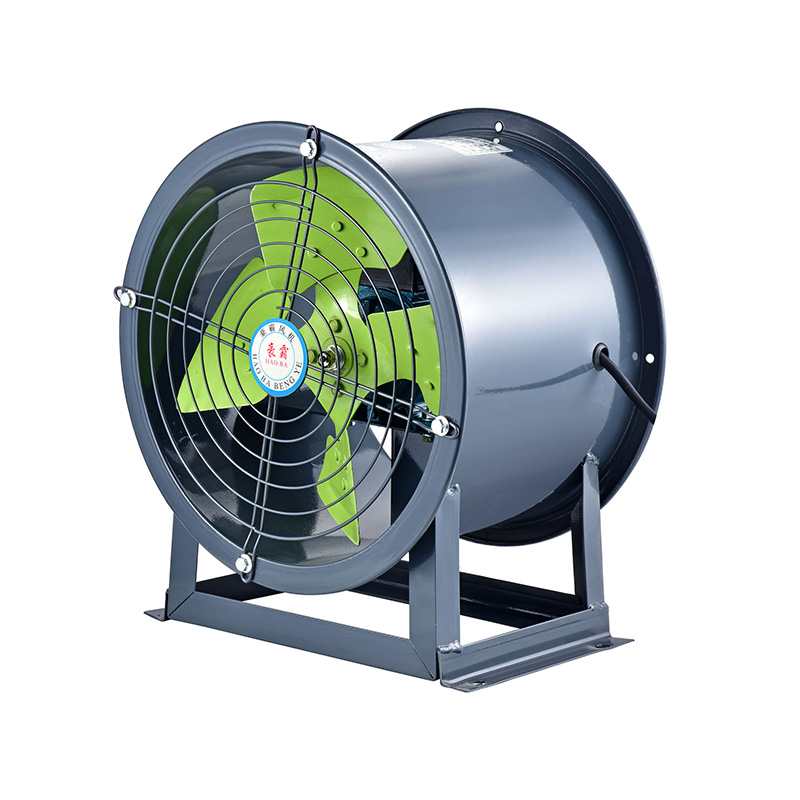
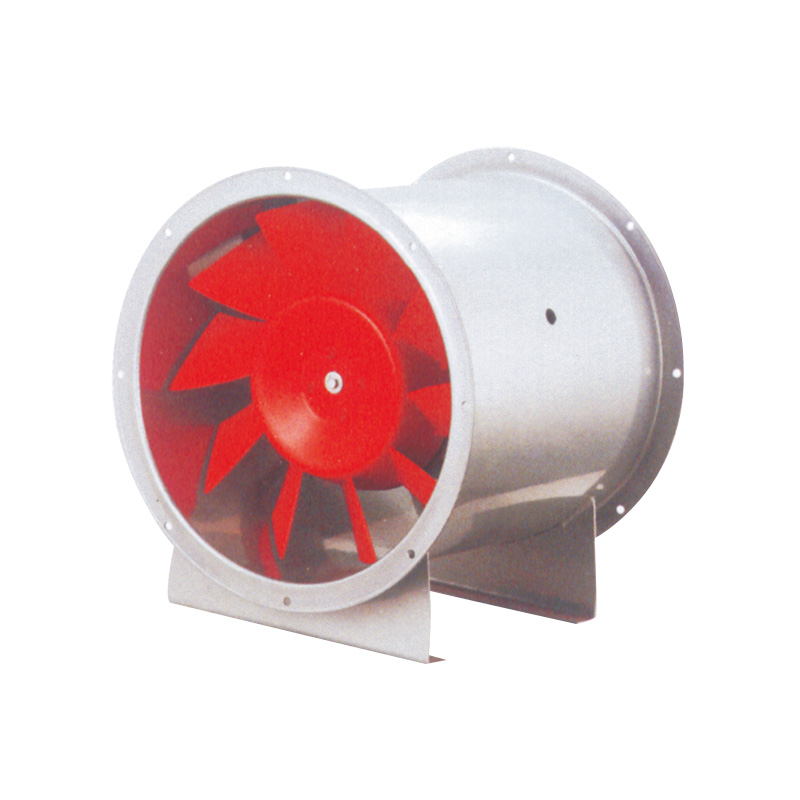
In contrast, an axial fan moves air parallel to the axis of rotation. This allows for a higher volume of airflow at lower pressure, which is ideal for general ventilation, cooling large open spaces, or providing fresh air in warehouses and workshops. Because axial fans typically have a simpler design with fewer parts than centrifugal fans, they often consume less energy when properly sized for the task.
Industrial facilities often face the challenge of balancing airflow demands with energy consumption. Integrating energy-efficient high speed industrial fans can address this by using variable frequency drives (VFDs) that adjust the fan speed according to real-time ventilation needs. This approach avoids running fans at full speed unnecessarily, which reduces power usage and wear on the equipment.
Similarly, modern rotor fans are increasingly equipped with advanced motor technologies that reduce electricity consumption without sacrificing airflow. By optimizing blade shapes and motor efficiency, these fans maintain performance while lowering operational costs. In some cases, rotor fans can be retrofitted with energy-saving components, providing a cost-effective alternative to full replacement.
Choosing between a centrifugal fan and an axial fan depends on the specific environment and airflow requirements of the industrial facility. For example, processes that involve filtering or moving air through complex ductwork often benefit from the pressure capabilities of centrifugal fans. Their design makes it easier to overcome resistance and maintain consistent airflow, which is critical in systems requiring precise air quality control.
On the other hand, axial fans are better suited to applications where high volumes of air need to be moved in open areas without significant resistance. In large manufacturing floors or storage areas, axial fans can promote air circulation efficiently, reducing the need for multiple smaller fans and simplifying installation.
Maintenance and operational considerations also influence fan selection. High speed industrial fans typically require regular inspection due to the stresses involved in rapid rotation, but advancements in materials and design have improved their durability. Proper maintenance extends the life of rotor fans as well, especially because their integrated design can make repairs more straightforward.
In terms of energy efficiency, both centrifugal fans and axial fans benefit from careful matching to the system requirements. Oversized fans consume unnecessary energy, while undersized fans fail to provide adequate airflow. Utilizing airflow modeling and performance curves helps ensure that the selected fan operates within the more efficient range for the facility's needs.
In conclusion, industrial facilities have several energy-efficient fan options to consider. The high speed industrial fan, rotor fan, centrifugal fan, and axial fan each bring unique advantages depending on the airflow volume, pressure needs, and space constraints. By selecting fans that align well with operational demands and incorporating energy-saving features such as variable speed control, facilities can improve ventilation effectiveness while managing energy consumption. This approach supports both environmental goals and cost management without compromising workplace conditions.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى