How Proper Fan Selection Helps Meet Emission Standards
2025-07-08
A variety of fan types are available to serve different ventilation needs, including roof ventilator wind turbine units, blower axial models, and high output blowers. Each type offers unique advantages depending on the application, and understanding their specific capabilities helps in designing systems that support emission compliance.

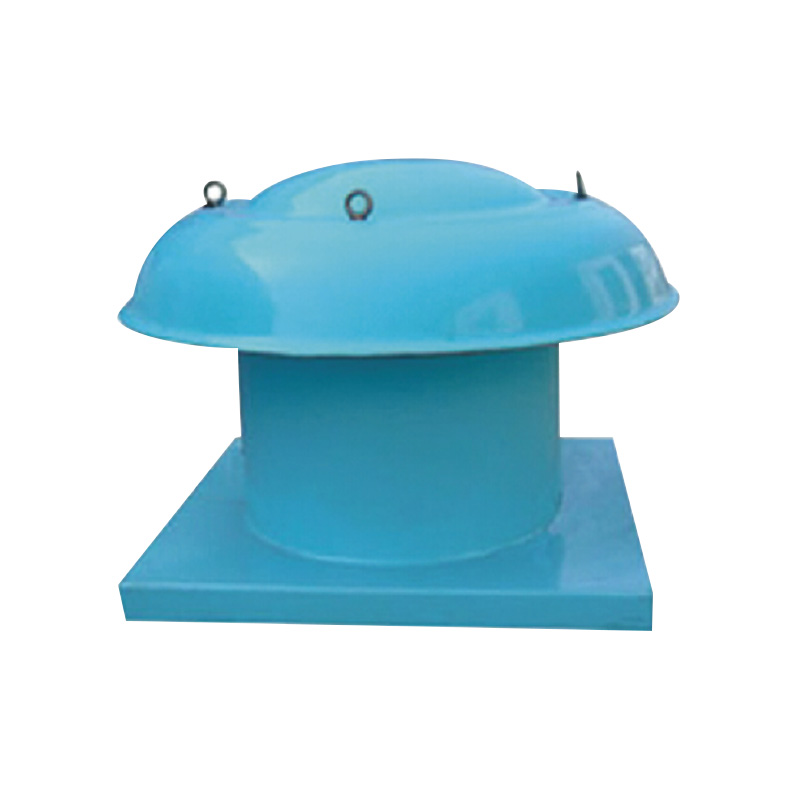
Roof ventilator wind turbines are widely used for natural ventilation in commercial and industrial buildings. They work by harnessing wind energy to pull stale or contaminated air out of a facility without the need for additional electrical power. This passive approach reduces energy consumption while maintaining airflow. Properly sizing and installing roof ventilator wind turbines ensures that emissions such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter are effectively removed from indoor environments, helping facilities stay within regulatory limits.
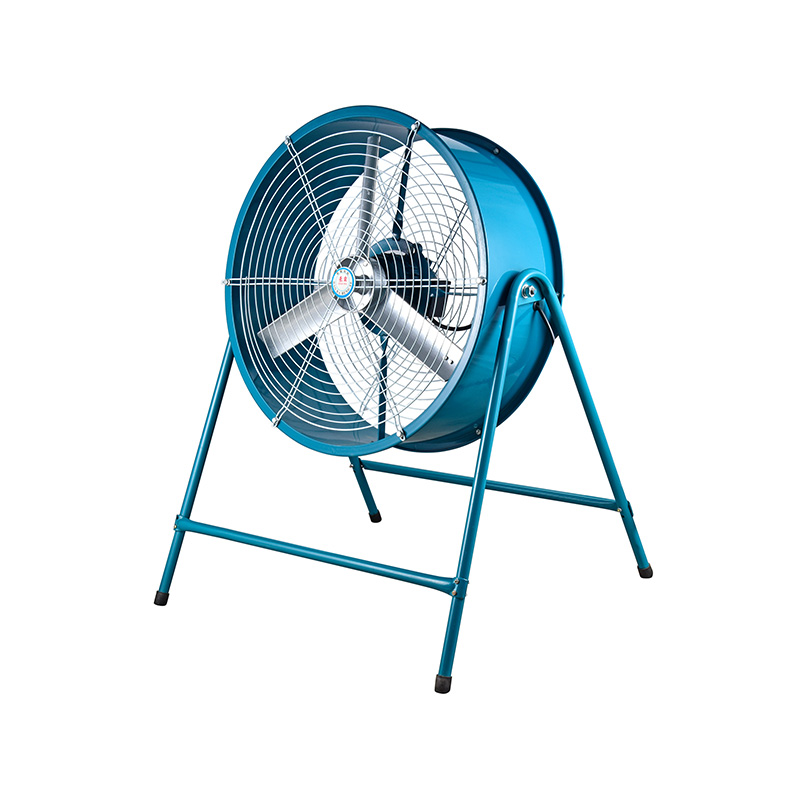
Blower axial fans, on the other hand, are mechanical devices that push air parallel to the fan’s axis, creating a continuous flow that can be directed precisely where needed. These fans are often used in systems requiring consistent airflow at moderate pressures, such as in chemical plants or manufacturing lines. Selecting the correct blower axial fan is crucial because inadequate airflow can result in poor pollutant extraction, pilot to higher emission levels. Conversely, oversized fans can waste energy and increase operational costs without proportional environmental benefits.
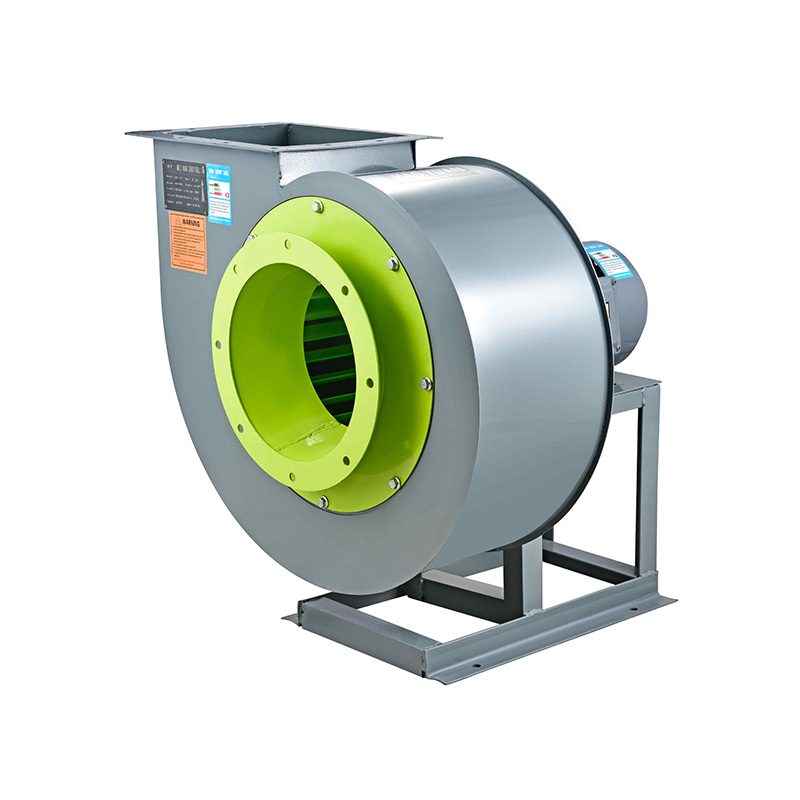
For situations that demand more powerful ventilation solutions, high output blowers come into play. These units generate increased air volume and pressure, making them suitable for applications where large-scale contaminant removal is necessary. High output blowers can efficiently manage emissions in processes such as combustion exhaust, dust collection, or fume extraction. Choosing a high output blower that matches the system requirements allows for better control over pollutant dispersal and ensures that emission levels remain within permissible thresholds.
Proper fan selection also involves considering factors such as noise levels, durability, and energy efficiency. For example, using roof ventilator wind turbines not only supports emission reduction but also less noise pollution since they operate without motors. Blower axial fans, when paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs), offer adjustable airflow that can be tailored to process demands, reducing unnecessary energy use while maintaining emission control. Similarly, selecting a high output blower with aerodynamic design features can improve airflow efficiency, further helping facilities comply with environmental standards.
Additionally, the layout of ventilation systems plays a significant role in emission management. A combination of roof ventilators, a wind turbine, and axial blower fans can provide a balanced solution where natural and mechanical ventilation complement each other. High output blowers can be integrated to handle peak pollutant loads or emergency ventilation needs. Such hybrid configurations require careful planning to ensure each component operates at its ideal capacity, avoiding underperformance that could compromise emission control efforts.
Routine maintenance is another important consideration tied to fan selection. Choosing robust models of roof ventilator wind turbines, blower axial fans, and high output blowers can reduce downtime and maintain consistent airflow over time. Regular inspection and cleaning prevent performance degradation that might increase emissions due to inadequate ventilation. Therefore, investing in reliable fan equipment with accessible maintenance options supports long-term compliance with emission standards.
In conclusion, the selection of appropriate fans and blowers is a key factor in helping facilities meet emission regulations. Roof ventilator wind turbines offer energy-saving natural ventilation, blower axial fans provide controlled mechanical airflow, and high output blowers address heavy-duty emission challenges. By understanding the strengths and applications of each fan type, engineers and facility managers can design ventilation systems that effectively reduce pollutants while optimizing energy use. This balanced approach not only protects the environment but also supports operational efficiency and regulatory compliance in various industrial settings.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى