Understanding Static Pressure In Fan Selection
2025-07-08
Selecting the right fan for a particular ventilation or air-moving application requires understanding several important factors, among which static pressure plays a crucial role. Whether you are choosing a power roof ventilator, a blower floor unit, or a blower for ventilation in a commercial or industrial setting, knowing how static pressure affects performance will help ensure that your system runs efficiently and meets airflow requirements.

Static pressure refers to the resistance to airflow within the ventilation system. It is essentially the force that a fan must overcome to push air through ducts, filters, grilles, or any other obstructions in the airflow path. This resistance impacts the fan’s ability to move air effectively. For example, a power roof ventilator installed on a building must overcome static pressure caused by the ductwork, weather dampers, and any filters or screens placed in the system. Ignoring static pressure can lead to poor ventilation performance and increased energy consumption.
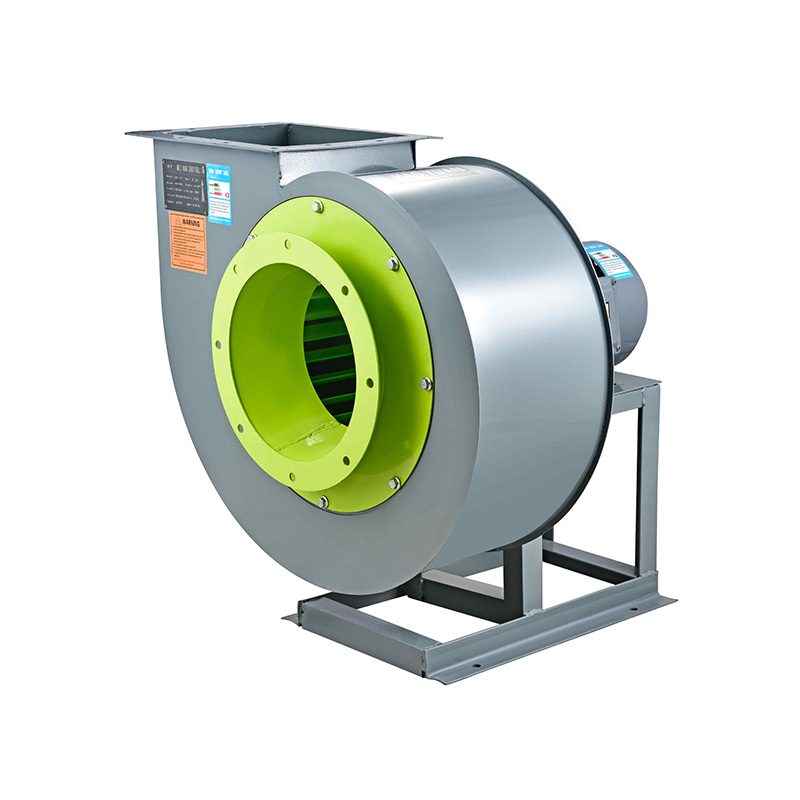
When selecting a blower for ventilation, understanding the static pressure is critical. The static pressure is typically measured in inches of water gauge (in. wg) or Pascals (Pa). Fan manufacturers provide performance curves that plot airflow against static pressure, allowing you to match a fan’s capabilities to your system’s needs. For a blower floor system, which often handles larger volumes of air at moderate pressures, knowing the static pressure helps you choose a unit that can maintain required airflow without overloading the motor or causing premature wear.
One common mistake in fan selection is assuming that airflow alone defines a suitable fan. However, a blower for ventilation operating at low static pressure might not deliver the same volume of air if installed in a system with higher resistance. The power roof ventilator, for example, must be carefully matched not only to the desired airflow but also to the expected static pressure in the rooftop duct system. Overlooking static pressure can lead to undersized or oversized equipment, resulting in inefficient operation and increased operational costs.
In practical terms, calculating static pressure requires a detailed understanding of your ventilation system’s layout. This includes the length and diameter of ducts, the number of bends and fittings, the type of filters, and any other components that restrict airflow. For blower floor units, the static pressure might also include resistance from inlet or outlet screens, louvers, or even the building envelope if air is being pulled from or expelled to outdoor environments.
Once you have an accurate estimate of static pressure, you can consult fan curves to select a blower for ventilation that meets your airflow and pressure requirements. A fan curve shows how much air a fan moves (usually in cubic feet per minute or CFM) at different static pressures. For instance, as static pressure increases, the airflow produced by the power roof ventilator decreases. By comparing your system’s static pressure against these curves, you can identify a fan that operates efficiently within your parameters.
It is also important to consider the operating range of the fan. Some power roof ventilators are designed to perform well at specific static pressure ranges, while others can handle a wider range. Choosing a blower floor or blower for ventilation that matches your typical system conditions will help maintain consistent airflow and reduce wear and tear on the fan components.
Regular maintenance can affect static pressure as well. For example, dust buildup on filters or inside ducts increases resistance, raising static pressure and reducing airflow. This is true for any fan type, including power roof ventilators and blower floor models. Monitoring static pressure over time can help you identify when maintenance is needed to keep the system running smoothly.
In some cases, installing adjustable dampers or variable frequency drives (VFDs) can help manage static pressure by controlling airflow dynamically. This allows a blower for ventilation to operate closer to its design point, reducing energy consumption and extending fan life. A power roof ventilator equipped with such controls can adapt to changing building conditions and ventilation demands without sacrificing performance.
In summary, static pressure is a fundamental factor when selecting any ventilation fan, including power roof ventilators, blower floor units, and blowers for ventilation systems. Understanding how static pressure influences airflow and fan performance helps avoid common issues such as inadequate ventilation, excessive noise, or increased energy use. Careful calculation and matching of static pressure with fan curves enable you to choose equipment that will operate efficiently and reliably over time.
By giving static pressure the attention it deserves in your fan selection process, you can improve the overall effectiveness of your ventilation system. Whether your project involves installing a new power roof ventilator or upgrading an existing blower floor setup, recognizing the impact of static pressure will guide you toward a practical, well-performing solution.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى