Fan Applications In Tunnel And Subway Ventilation
2025-07-08
Proper ventilation is a crucial aspect of tunnel and subway system design, directly impacting safety, air quality, and operational efficiency. Among the various ventilation equipment used, different types of fans play essential roles in maintaining airflow, controlling temperature, and removing harmful gases. This article explores the role of fans, especially focusing on centrifugal blower high pressure units, industrial blowers, and floor ventilators in tunnel and subway ventilation.
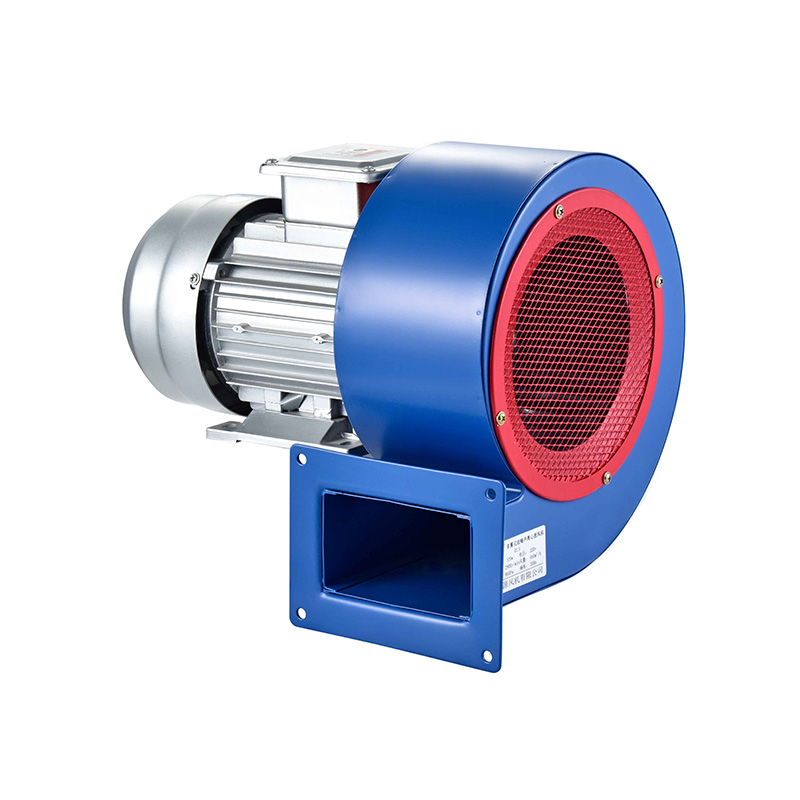
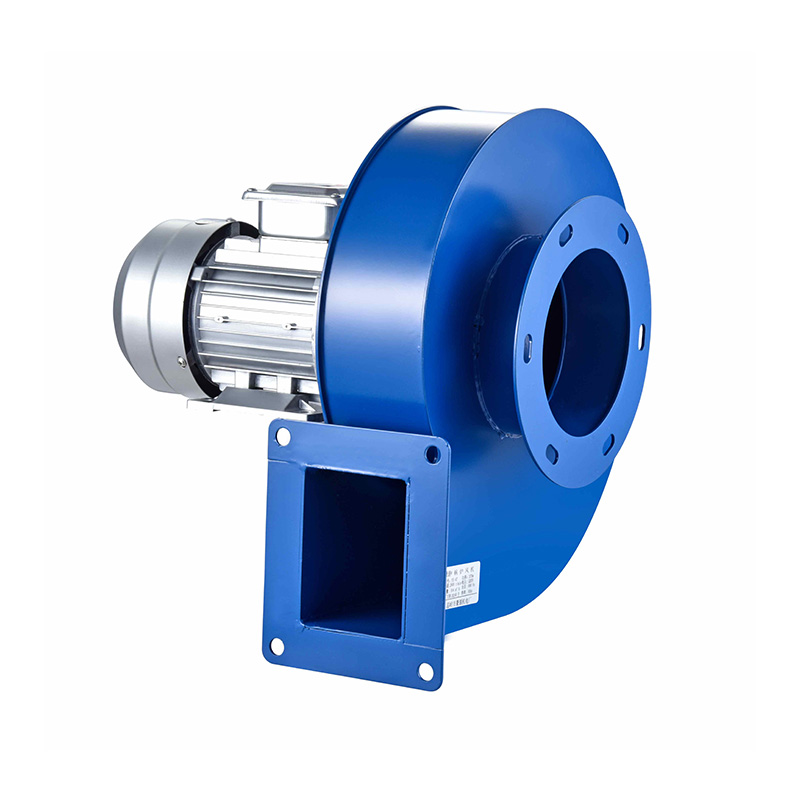
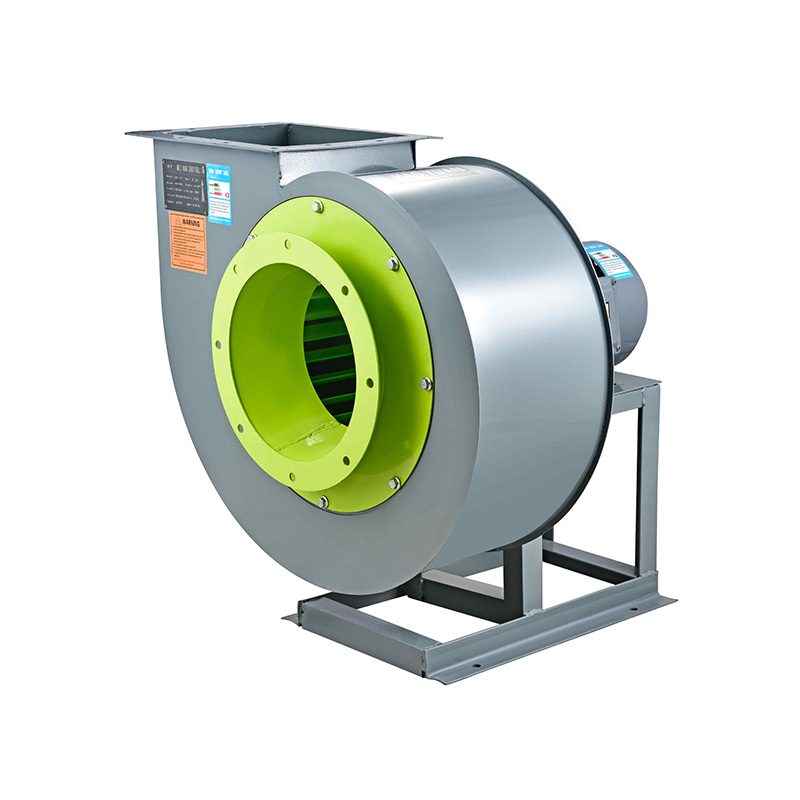
In underground environments such as tunnels and subways, air circulation must be carefully managed due to the confined space and the presence of pollutants like vehicle exhaust, dust, and other harmful gases. The centrifugal blower high pressure fan is frequently chosen for these settings because it can generate the necessary pressure to push air through long and narrow passages, overcoming resistance from tunnel walls and duct systems. Its design allows for high static pressure while maintaining reliable airflow, which is vital in subway tunnels where ventilation ducts can be extensive and complex.
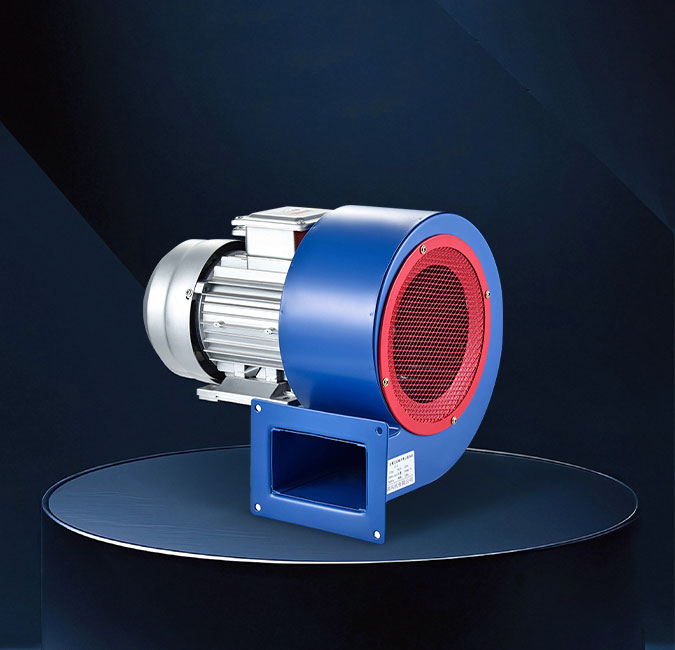
Industrial blowers also play an important role in tunnel ventilation. These blowers are designed for continuous operation under harsh conditions and can handle large volumes of air, making them suitable for both forced and exhaust ventilation systems. Industrial blowers used in subway tunnels are typically built with durable materials to withstand dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Their robust construction ensures consistent performance, which is essential for maintaining air quality and passenger comfort during peak hours.
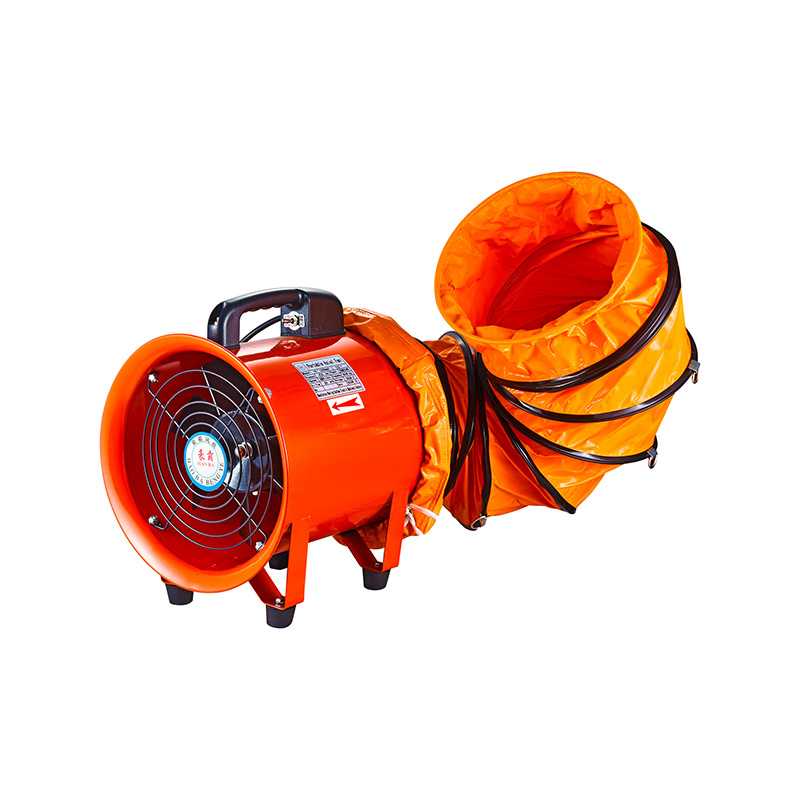
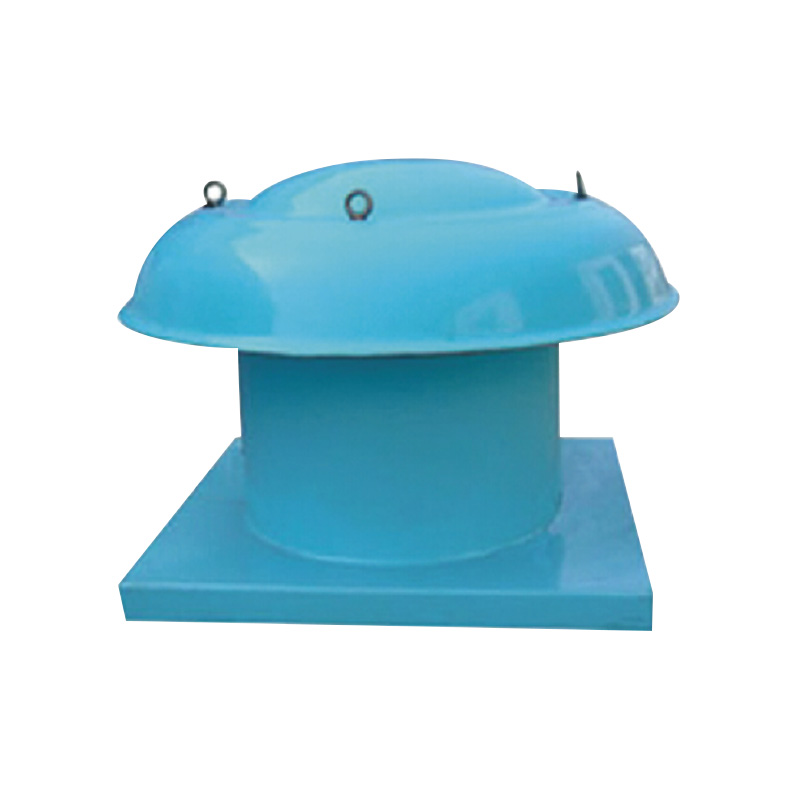
Floor ventilators serve as a complementary solution within the tunnel and subway ventilation schemes. Positioned at strategic locations along the tunnel floor or platforms, floor ventilators aid in localized airflow control and help reduce the stagnation of air near pedestrian areas. They contribute to a better distribution of fresh air and assist in directing smoke or exhaust gases away from critical zones during emergencies. While floor ventilators may not handle the main volume of air, their contribution to localized ventilation improves overall air circulation and safety.
One of the key challenges in tunnel ventilation is balancing airflow to ensure pollutants are adequately diluted and removed without causing excessive noise or energy consumption. The centrifugal blower high pressure units are effective in this regard due to their ability to generate controlled pressure levels, allowing the system to maintain steady airflow rates. These fans are often integrated into larger ventilation networks, working alongside industrial blowers and floor ventilators to create a comprehensive air management system.
During emergency situations such as fires or toxic gas leaks, ventilation fans must quickly and efficiently evacuate harmful substances while maintaining breathable air for evacuation routes. Centrifugal blower high pressure fans are typically installed in these systems to provide rapid smoke extraction and maintain pressure differentials to keep smoke from spreading to passenger areas. Their capacity to operate under high resistance makes them reliable components in emergency ventilation.
Industrial blowers contribute to day-to-day ventilation needs by handling large air volumes required for routine air exchange. These blowers are generally placed at tunnel entrances or ventilation shafts where they intake fresh air or expel stale air. Their design focuses on durability and energy efficiency, helping to keep operating costs manageable while ensuring continuous ventilation. Industrial blowers also facilitate temperature control by circulating cooler air during warmer months and distributing heat when necessary.
Floor ventilators complement these primary ventilation fans by addressing air quality at the ground level. They are particularly effective in subway platforms where passenger density is high and air quality can degrade quickly without adequate ventilation. The use of floor ventilators helps create comfortable conditions by fewer pockets of stale air and improving overall circulation in areas where fixed ductwork is limited or impractical.
Maintenance and reliability are important considerations when selecting fans for tunnel and subway ventilation. Centrifugal blower high pressure units are favored for their ease of maintenance and stable performance under varying loads. Industrial blowers, with their robust design, often require little upkeep, reducing downtime in critical ventilation systems. Floor ventilators, typically smaller and more localized, can be inspected and serviced without major disruption to operations.
In summary, the combined use of centrifugal blower high pressure fans, industrial blowers, and floor ventilators forms an effective ventilation strategy for tunnels and subway systems. Each type of fan addresses different aspects of airflow management — from generating high-pressure airflow to distributing air locally and maintaining air quality near pedestrian areas. Proper integration of these fans ensures the ventilation system meets safety standards, provides comfort, and supports efficient tunnel operation.
Ventilation technology continues to evolve with a focus on energy efficiency and environmental impact, but the fundamental roles of centrifugal blower high pressure units, industrial blowers, and floor ventilators remain central to tunnel and subway design. By understanding the functions and appropriate applications of these fans, engineers and facility managers can develop ventilation systems that perform reliably under demanding underground conditions.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى