High Flow Axial Fan Pressure Gain Explained
2025-12-05
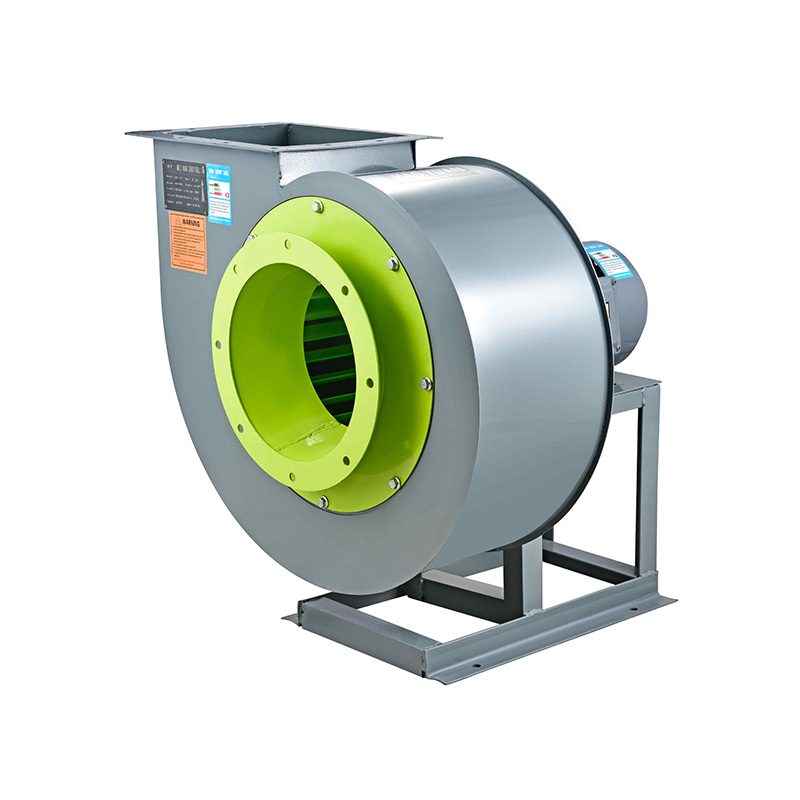
Understanding the pressure characteristics of high flow axial fan and vane axial flow fan is crucial for achieving effective ventilation solutions. From open-space cooling to complex ducted systems, selecting the correct fan type and maintaining it properly ensures operational efficiency and longevity. Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd. continues to deliver advanced ventilation equipment tailored to meet diverse industrial and commercial needs, combining robust engineering with reliable performance.
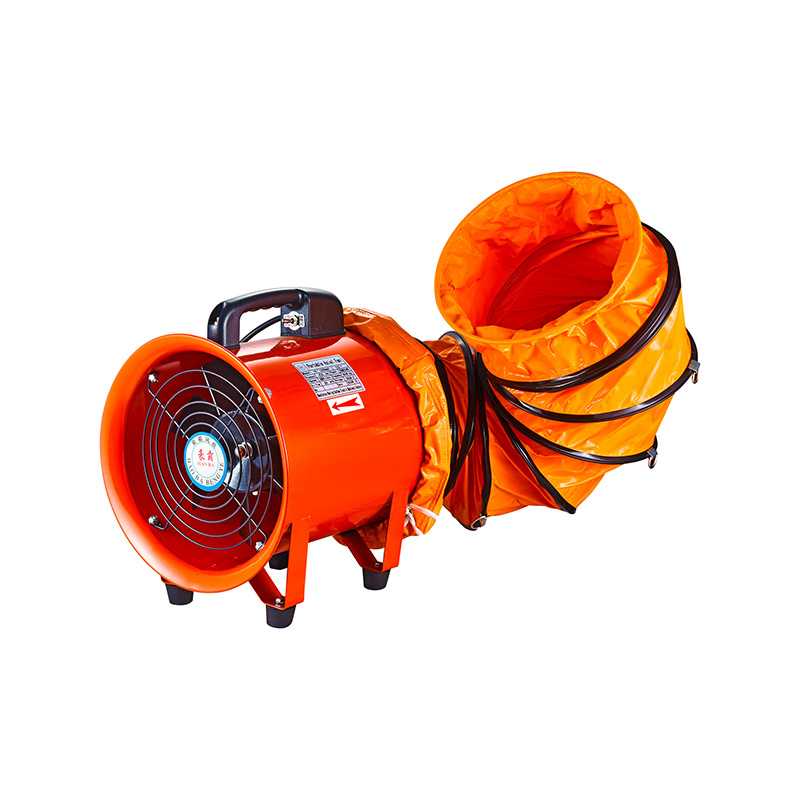
1. How High Flow Axial Fans Achieve Pressure Gain
High flow axial fans generate pressure primarily through the rotation of blades, imparting kinetic energy to the air. While these fans are designed to handle large air volumes efficiently, their static pressure is typically limited due to the nature of axial flow design. To increase pressure gain:
- Blade geometry can be optimized for specific airflow requirements.
- Pitch angle adjustments allow the fan to provide more resistance against airflow, thereby increasing pressure.
- Maintaining clean and well-balanced blades ensures consistent performance and prevents efficiency loss.
The result is a fan capable of delivering a steady stream of air, suitable for ventilation shafts, cooling systems, and large halls.
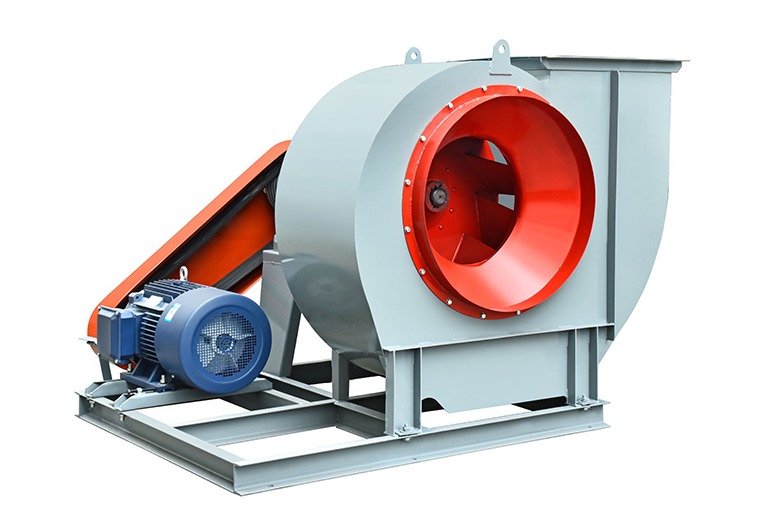

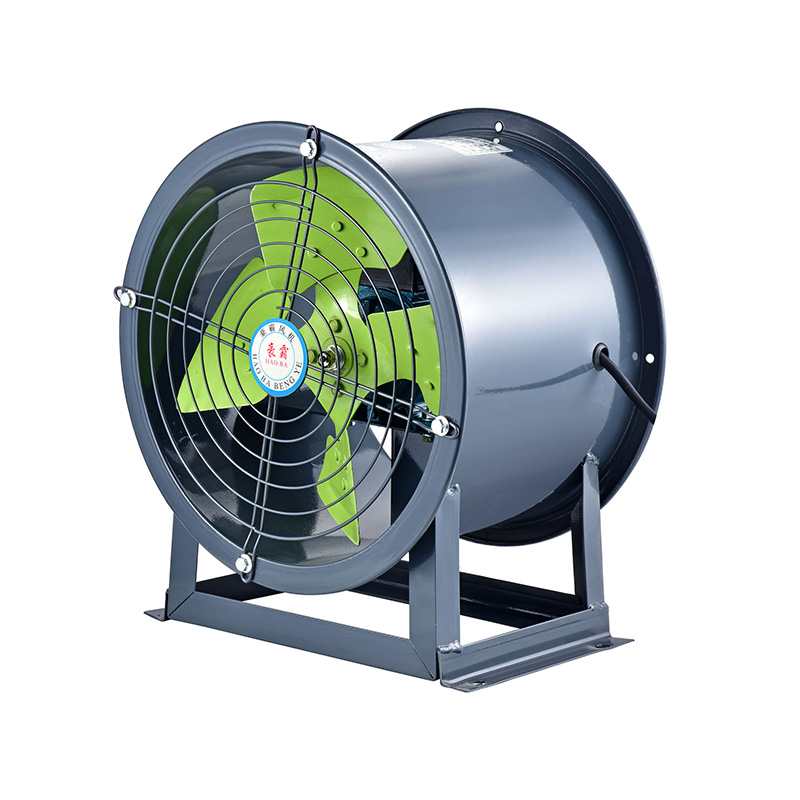
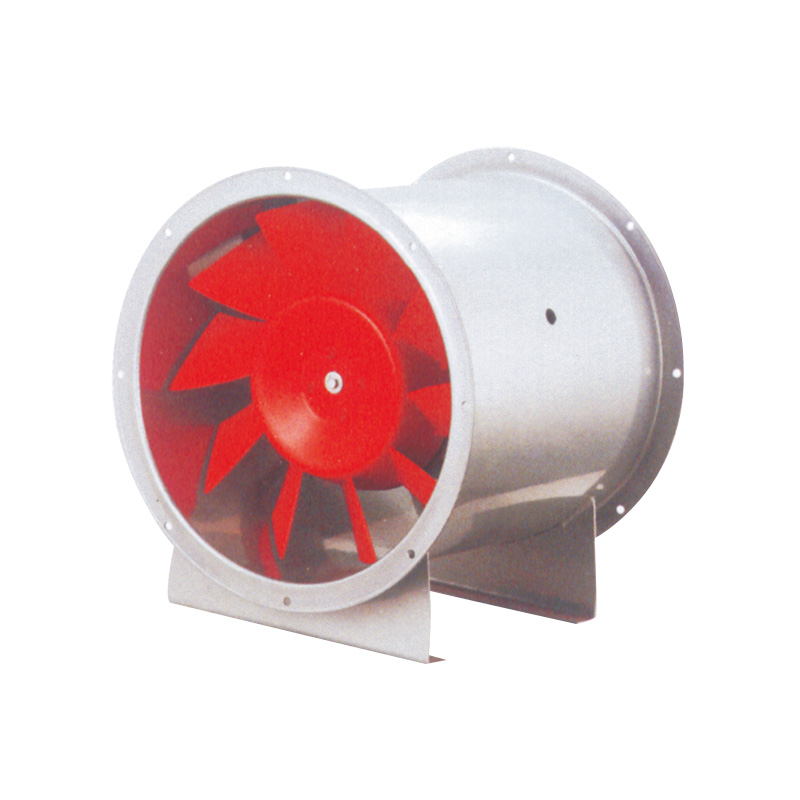
2. The Role of Vane Axial Flow Fans in Static Pressure Enhancement
Vane axial flow fans include guide vanes or stators positioned downstream of the rotor. These vanes reduce the swirl created by rotating blades, converting rotational energy into static pressure. Key benefits include:
- Increased static pressure: Ideal for ducted systems with resistance.
- Improved airflow stability: Reduces turbulence and noise in the ventilation system.
- Energy efficiency: By recovering kinetic energy, these fans achieve similar airflow with less power consumption.
By integrating vane axial flow fans in ducted installations, facilities can achieve higher system pressures without resorting to larger or more energy-intensive fans.
3. Comparing High Flow Axial Fans and Vane Axial Flow Fans
While both fans share the axial design, their applications differ:
- High Flow Axial Fans: nicely for open or low-resistance environments where volume is prioritized over pressure.
- Vane Axial Flow Fans: Suitable for ducted systems or applications where pressure gain is critical.
- Maintenance: Both require regular cleaning of blades and inspection of bearings, but vane axial flow fans also benefit from periodic guide vane checks to ensure efficiency is maintained.
Choosing the correct fan type depends on system requirements, space constraints, and energy considerations.
4. Maintenance Tips for good Performance
Regular maintenance extends fan lifespan and maintains efficiency:
- Blade cleaning: Dust and debris accumulation reduces airflow and pressure gain.
- Bearing lubrication: Ensures smooth rotation and reduces vibration.
- Tightening fasteners: Prevents blade misalignment, which can compromise both high flow axial fan and vane axial flow fan performance.
- System inspection: Check ductwork for leaks or blockages that can affect static pressure and airflow.
At Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd., we provide guidance on fan maintenance schedules to ensure consistent operation in demanding industrial environments.
5. Selecting the Correct Fan for Your Application
When designing a ventilation system:
- Evaluate airflow and pressure requirements carefully.
- Consider the environment: open versus ducted applications.
- Balance energy consumption with airflow and pressure needs.
- Factor in maintenance accessibility and long-term reliability.
High flow axial fans are typically selected for high-volume, low-resistance applications, while vane axial flow fans are preferred when static pressure and efficiency recovery are required. By choosing the Correct fan type, facilities can achieve reliable airflow, lower operational costs, and reduced energy consumption.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى