Vane Axial Flow Fan vs Standard Axial Fan Performance
2025-12-12
Comparing high flow axial fan and vane axial flow fan performance highlights the importance of understanding system requirements, airflow characteristics, and static pressure demands. Both fans have advantages in specific contexts, and Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd. provides comprehensive solutions for diverse industrial and commercial ventilation needs. Proper selection and maintenance ensure that these fans deliver stable, efficient, and long-lasting performance.
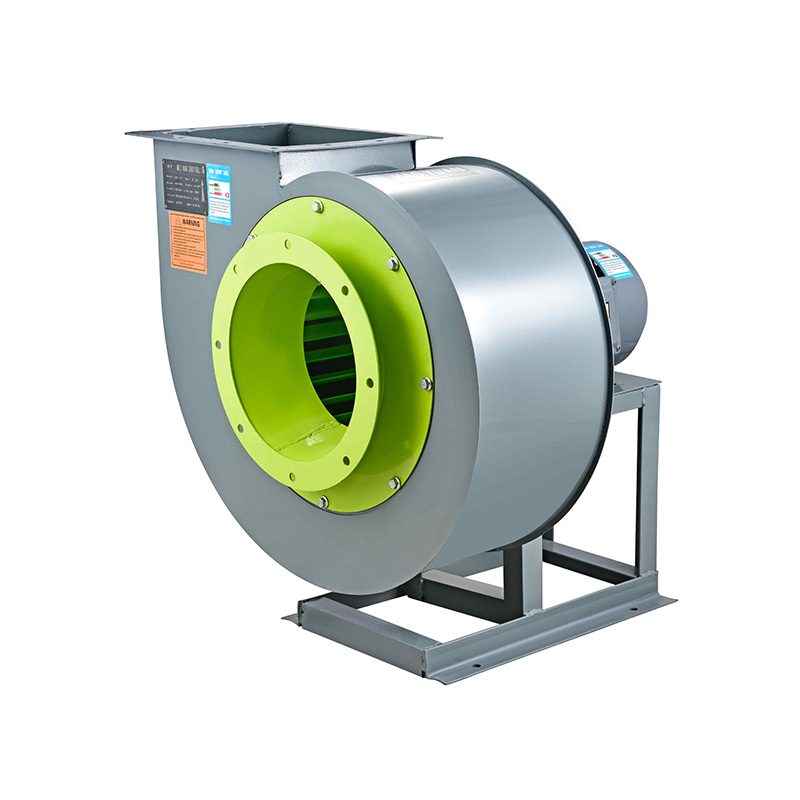
1. Design Differences Between Standard Axial Fans and Vane Axial Flow Fans
Standard axial fans consist of rotating blades mounted on a hub. Air is accelerated along the axis by the blade rotation. Key characteristics include:
- High volume airflow capacity.
- Simple mechanical structure with fewer components.
- Lower initial cost and ease of installation.
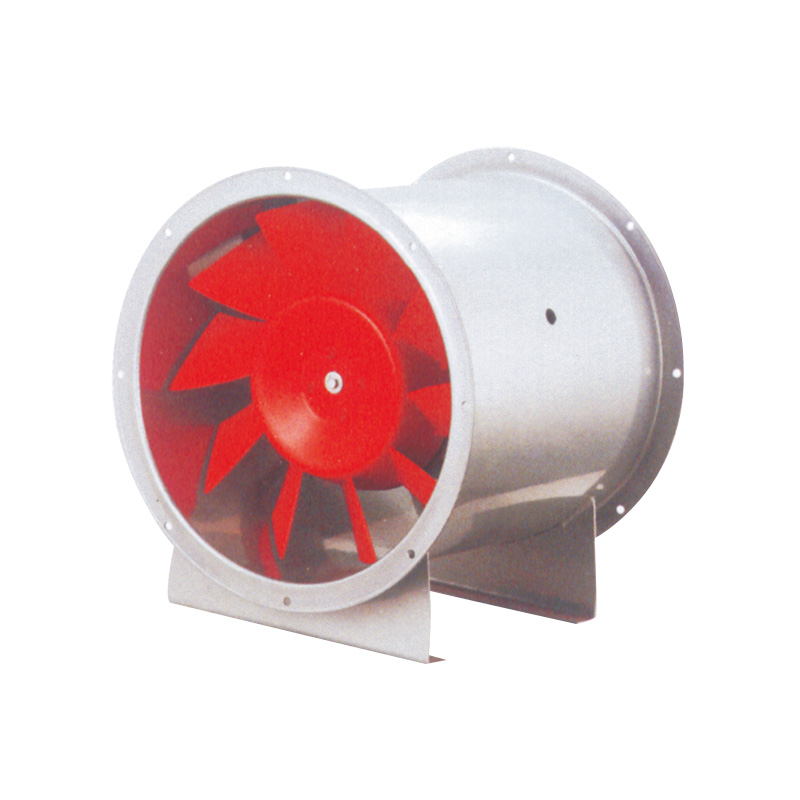
Vane axial flow fans add a set of stationary guide vanes downstream of the rotor. These vanes serve to:
- Redirect airflow, reducing rotational turbulence.
- Increase static pressure without increasing energy consumption.
- Improve efficiency in ducted or high-resistance systems.
This design enhancement allows vane axial flow fans to operate more effectively in applications where airflow must overcome resistance in ducts or filters.
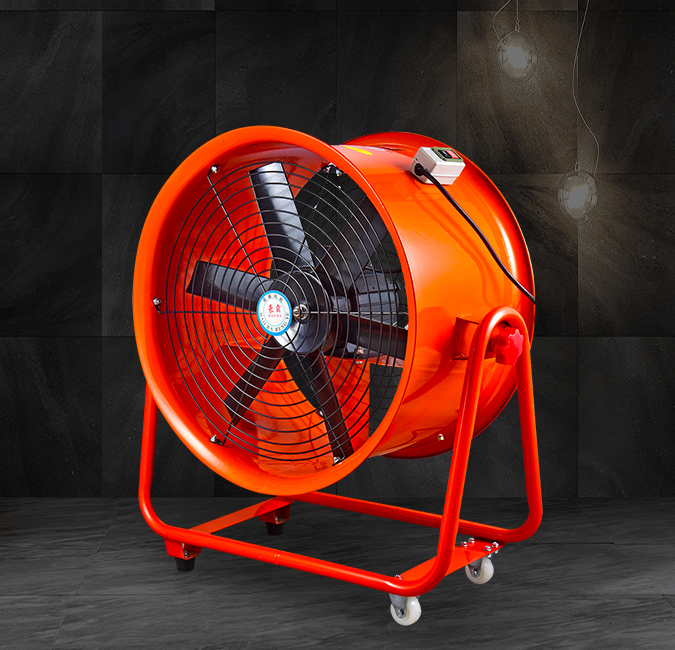

2. Airflow and Pressure Performance Comparison
Performance differences between the two fan types are evident in real-world applications:
- High Flow Axial Fan: Typically delivers large volumes of air at relatively low static pressure. Ideal for open spaces, large halls, or cooling towers where airflow volume is more critical than overcoming resistance.
- Vane Axial Flow Fan: Converts some of the rotational energy of the air into static pressure, allowing the system to achieve higher pressures at comparable airflow rates. This makes them suitable for ducted systems, ventilation tunnels, or industrial processes requiring precise airflow control.
By understanding these differences, engineers can match the fan to the system needs, improving energy efficiency and overall performance.
3. Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy consumption is a major factor in fan selection:
- Standard Axial Fans: Efficient for open-air applications but may require higher motor power if ductwork or resistance is present.
- Vane Axial Flow Fans: Guide vanes reduce swirl losses and improve the conversion of rotational energy into useful airflow, result in better energy efficiency in ducted systems.
Proper fan selection ensures that operational costs remain manageable while maintaining reliable performance.
4. Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Another important consideration is operational noise:
- Standard Axial Fans: Can generate higher turbulence-induced noise, particularly at higher speeds.
- Vane Axial Flow Fans: Guide vanes help smooth airflow, reducing turbulence and associated noise levels.
Regular maintenance, including blade cleaning and bearing lubrication, is essential for both fan types to minimize noise and vibration over time.
5. Maintenance and Longevity
Maintenance requirements differ slightly between the two designs:
- High Flow Axial Fan: Periodic inspection of blades, hub, and bearings. Clean blades to prevent airflow reduction.
- Vane Axial Flow Fan: In addition to standard maintenance, check guide vanes for alignment and integrity, as damaged vanes can affect airflow distribution and pressure.
Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd. provides guidance and support for fan maintenance to help clients achieve good performance and longevity for both fan types.
6. Selecting the Appropriate Fan Type
Selecting the correct fan type involves evaluating several factors:
- Application environment: open vs. ducted.
- Required airflow volume and static pressure.
- Energy consumption and operational efficiency.
- Maintenance accessibility and long-term reliability.
For applications where airflow volume dominates, high flow axial fans are preferred. For systems requiring higher static pressure and smoother airflow, vane axial flow fans offer tangible advantages.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى