How Blower Wheels Affect Air Volume And Pressure
2025-07-08
In industrial ventilation systems, blower wheels play a crucial role in determining the performance of fans and blowers. Whether it’s a centrifugal ventilator, an industrial exhaust blower, or a factory ventilation fan, the blower wheel is the heart of the airflow generation process. Understanding how blower wheels influence air volume and pressure is essential for designing efficient ventilation systems and ensuring effective air movement in various industrial environments.

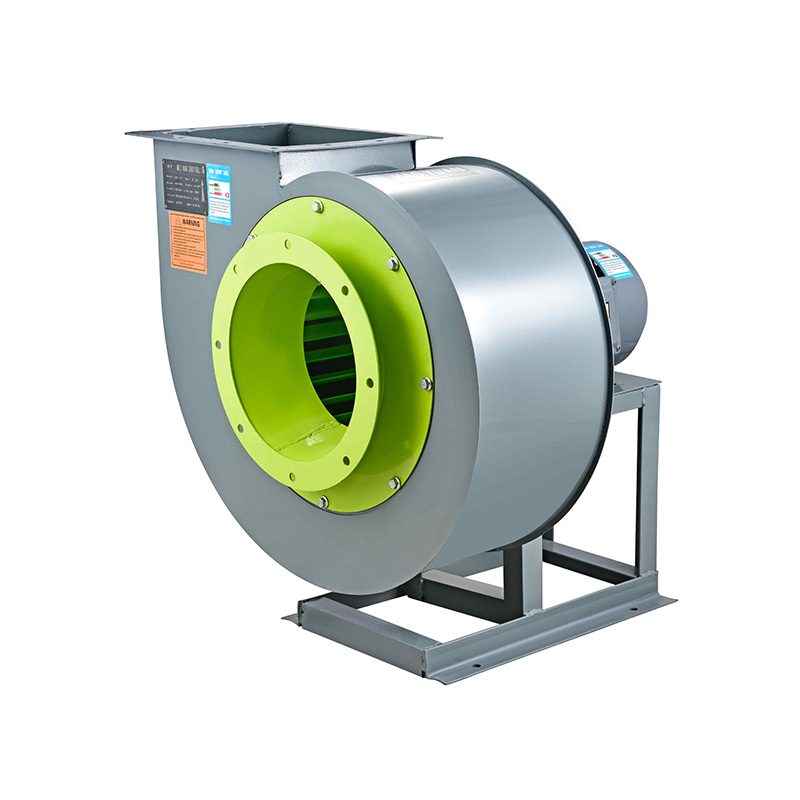
A blower wheel is the rotating component that moves air by converting mechanical energy into kinetic energy. Its design—shape, size, and rotation speed—directly impacts the air volume (the amount of air moved) and the pressure (the force that drives the air through ducts and filters). In a centrifugal ventilator, for instance, the blower wheel draws air into the center of the wheel and pushes it outwards through centrifugal force. This action creates a steady flow of air, making centrifugal ventilators suitable for many industrial exhaust applications.
One of the primary ways blower wheels affect performance is through their geometry. The diameter and width of the wheel influence the volume of air it can move. A larger diameter blower wheel generally moves more air because it sweeps a bigger area. However, increasing the size also changes the pressure characteristics. For example, in an industrial exhaust blower, a wider wheel can increase static pressure, which is necessary to push air through complex ductwork or filtration systems found in factories.
The shape of the blades on a blower wheel also plays a key role. Forward-curved blades typically move a higher volume of air at lower pressure, which can be ideal for certain factory ventilation fans that prioritize airflow over pressure. Backward-curved blades, on the other hand, are designed to produce higher pressure with a more efficient airflow rate, commonly used in industrial exhaust blowers that need to overcome resistance in ventilation systems. The blade angle and curvature influence how much air is accelerated and in which direction, thereby affecting both volume and pressure.
Rotation speed is another important factor. The faster the blower wheel spins, the greater the air volume and pressure it can generate. However, this relationship is not linear—doubling the speed more than doubles the pressure, but also increases energy consumption and noise levels. In centrifugal ventilators, managing the speed is a balance between achieving the desired airflow and maintaining system efficiency. Variable speed drives are sometimes used to optimize blower wheel operation in factory ventilation fans, allowing adjustment based on real-time ventilation needs.
The material and construction of blower wheels can impact performance indirectly. For example, blower wheels made of lightweight materials reduce the inertia and allow quicker acceleration, which can be beneficial in industrial exhaust blowers where quick responsiveness is required. However, durability must also be considered, especially in harsh environments where factory ventilation fans may encounter dust, moisture, or chemicals.
When selecting or designing a blower wheel for a centrifugal ventilator, it is essential to consider the specific air volume and pressure requirements of the application. For instance, an industrial exhaust blower in a manufacturing plant may require higher static pressure to overcome duct losses, while a factory ventilation fan in a warehouse might prioritize higher airflow to ensure adequate air exchange. Choosing the right blower wheel geometry and size will directly influence the system’s ability to meet these needs.
Maintenance and wear can also affect blower wheel performance over time. Accumulated dust or debris on the blades of a centrifugal ventilator can reduce efficiency, lowering air volume and pressure output. Similarly, imbalance caused by damage or wear on an industrial exhaust blower’s wheel can lead to vibrations and reduced lifespan. Regular inspection and cleaning help maintain the good performance of factory ventilation fans.
In conclusion, blower wheels are fundamental components that significantly affect the air volume and pressure generated by centrifugal ventilators, industrial exhaust blowers, and factory ventilation fans. Their size, blade shape, speed, and material all combine to influence airflow characteristics. Understanding these factors can help engineers and facility managers design and maintain ventilation systems that meet the specific demands of their industrial environments while ensuring efficient operation over time.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى