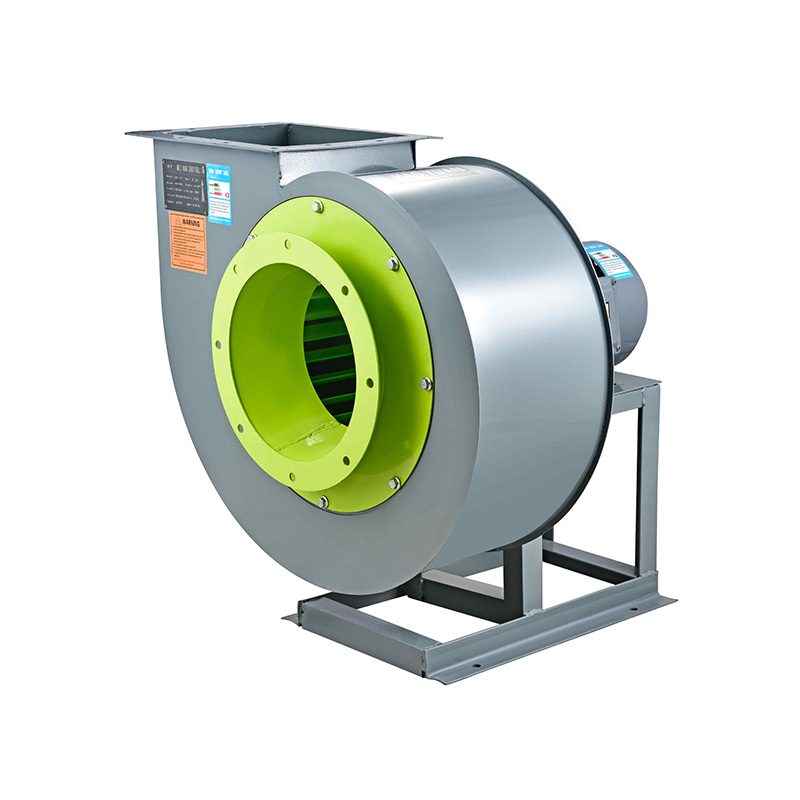
Why Vane Axial Flow Fan Boosts Static Pressure
2025-12-26
The use of guide vanes in vane axial flow fans effectively boosts static pressure, improves airflow stability, and enhances energy efficiency compared to standard high flow axial fans. Understanding these mechanisms allows engineers to design and maintain ventilation systems that deliver reliable performance. With advanced design and manufacturing, Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd. offers fans that meet diverse industrial, commercial, and HVAC requirements.
1. How Guide Vanes Work
Vane axial flow fans use stationary guide vanes positioned immediately after the rotating blades. Their function is to:
- Reduce Swirl: The rotor imparts a rotational component to the air, which does not contribute to forward pressure. The vanes redirect the swirl into axial flow.
- Convert Kinetic Energy: The redirected air increases static pressure without adding energy to the rotor.
- Improve Efficiency: By minimizing turbulence and swirl losses, the fan can maintain higher airflow at lower energy consumption.
The integration of guide vanes allows the fan to generate a higher static pressure than a comparable standard high flow axial fan.

2. Static Pressure Benefits in Ducted Systems
In ducted ventilation systems, airflow encounters resistance from bends, grilles, filters, and other components. Vane axial flow fans provide advantages in these scenarios:
- Stable Airflow: The vanes straighten the air stream, reducing turbulence and pressure drop along the duct.
- Enhanced System Performance: Higher static pressure enables the fan to overcome system resistance and maintain desired airflow rates.
- Versatility: Vane axial flow fans can be tailored for various duct sizes, air velocities, and pressure requirements, making them suitable for industrial, commercial, and HVAC applications.
3. Design Considerations for Static Pressure Enhancement
Several design elements influence the static pressure performance of vane axial flow fans:
- Rotor Blade Angle: Adjusting the pitch of the rotor blades can optimize airflow velocity and initial pressure.
- Guide Vane Geometry: The shape, number, and angle of the vanes determine how efficiently rotational energy is converted to static pressure.
- Fan Diameter and Speed: Larger diameters or higher rotational speeds can increase airflow, but the vane configuration ensures this energy is effectively used.
By balancing these parameters, engineers can design vane axial flow fans that meet specific pressure and airflow goals.
4. Practical Applications and Advantages
Vane axial flow fans are widely applied in environments requiring consistent static pressure:
- Industrial Ventilation: Factories and production lines with long ductwork benefit from enhanced static pressure.
- HVAC Systems: Air handling units often require higher pressure to distribute air evenly through complex duct networks.
- Cooling Systems: Vane fans are used in machinery cooling where duct resistance could limit airflow from a standard high flow axial fan.
In all cases, the inclusion of vanes allows for stable and reliable airflow performance.
5. Maintenance and Performance Optimization
To maintain static pressure performance over time:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust or debris on blades or vanes can reduce airflow and pressure.
- Alignment Checks: Proper rotor and vane alignment is crucial for pressure conversion efficiency.
- Bearing Maintenance: Smooth rotation of the rotor supports consistent airflow and reduces vibration.
Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd. provides guidance on maintenance procedures to ensure long-term performance of both high flow axial fans and vane axial flow fans in demanding industrial settings.
In modern ventilation systems, understanding the mechanisms behind high flow axial fan and vane axial flow fan performance is essential for engineers and designers. At Taizhou Haoba Electromechanical Co., Ltd., our engineering team focuses on optimizing fan design to achieve improved pressure performance without compromising airflow efficiency.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى